Breast Lift
• Mastopexy • Breast Lift • Ptosis • Sagging breasts •
Breast Lift – Mastopexy
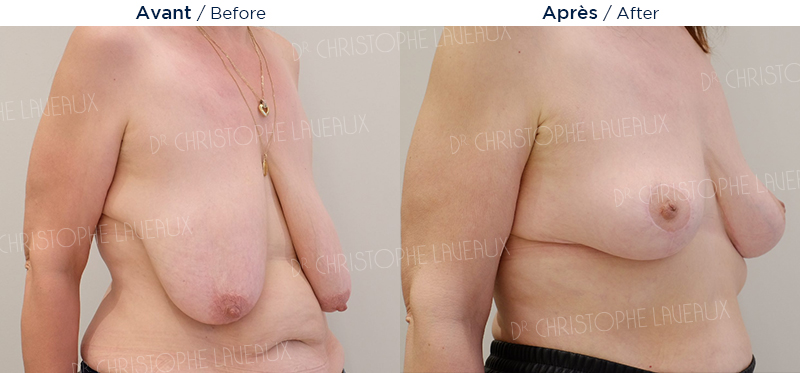
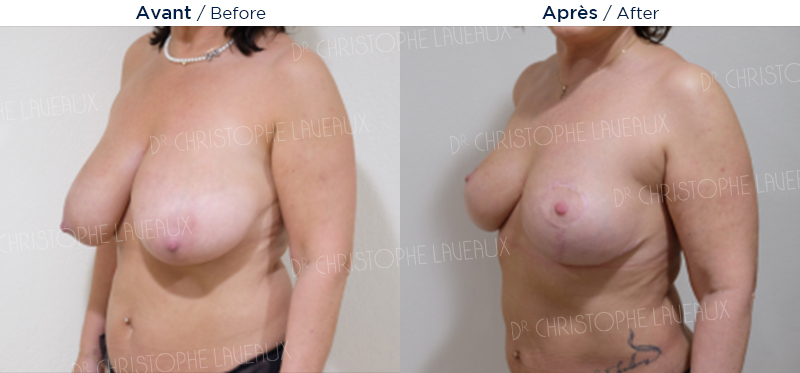
Low hanging breasts can be surgically reshaped. Ptosis or breast sag is when the areola is located too low and the stretched out skin is too large for glandular tissue. The breast seems empty (droopy breasts).
Breast ptosis usually occurs after weight loss or pregnancy with breastfeeding. The natural ageing of the chest also promotes ptosis. The volume of breast ptosis can be considered normal, too large (Mammary hypertrophy from ptosis) or too small (Mammary hypoplasia from breast ptosis).
The procedure is performed under general anaesthesia and lasts from 1 and a half to 3 hours. Hospitalisation ranges from 10 to 24 hours. Surgical intervention (treatment of ptosis or breast lift) repositions the nipple and areola to the correct height, lifts the breast and removes excess skin. The breast is raised, firmer and more beautiful.
Depending on the profile and the request of the patient, Dr. Laveaux offers an optional alternative technique to obtain a firmer breast and a more generous cleavage (slight “bimbo” effect).
To achieve this breast reshaping, the cosmetic surgeon is required to cut the skin, which causes scarring. The severity of the scars is proportional to the degree of ptosis :
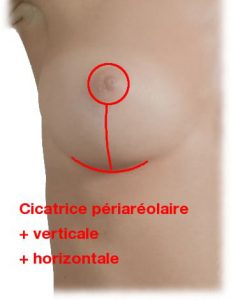
- for mild ptosis, a periareolar scar around the areola, where the lighter skin meets the darker skin may be sufficient;
- for moderate ptosis, an additional vertical scar is necessary, from the areola to the fold under the breast;
- for major ptosis, an inverted T scar (navy anchor scar) is mandatory. It combines a periareolar scar, a vertical scar and a more or less horizontal scar located in the fold under the breast.
The vertical “lollipop” technique, very often used by Dr. Laveaux, avoids or at least limits horizontal scarring in cases where it would have been necessary. A small touch-up under local anaesthesia is sometimes necessary a few months after the procedure, nevertheless this technique makes it possible to prevent a large horizontal scar.
- Mammary Hypertrophy treatment : if the breasts are too large, the surgeon may remove a certain amount of gland during the treatment of ptosis;
- Breast Implants: in the case of associated stunting or asymmetry between the two breasts, the surgeon can place the implant either during the same operation or during a separate procedure in order to give the breasts sufficient volume;
- Lipomodelage: fat injections can be performed either in the same operation or at a later time as is most often done to increase the breast size or simply improve the neckline.
Complete healing – Within 2 to 3 weeks
The after-effects are slightly painful requiring only simple analgesics. Edema (swelling), ecchymosis (bruises) and a hindrance to elevate the arms are frequent in the early stages. A compression bandage is applied on leaving the operating room (type of elastic bustier made to measure). It will be replaced before the patient leaves the clinic or at the first appointment. In rare cases, a drain can be inserted. It is removed before the patient leaves the clinic.
The concealed stitches are dissolvable. Some small stitches may be removed between the first and third week. The dressings are semi-permeable, so showers are allowed. Special adhesive dressings will be applied to the scars for 2-3 months in order to improve their appearance. Returning to work is possible between 5-10 days after surgery depending on the job. The patient may resume sporting activities after 6 weeks. A bra must be worn 24 hours a day for 1 month.
The aesthetic, functional, and psychological improvements are always very satisfactory after a breast lift operation. The shape of the breast will be permanent and the scars will be fully developed, that is, discreet, one year after the operation
As with any cosmetic surgery, complications can occur with a breast lift operation. But the likelihood of these complications is reduced in the hands of a qualified plastic surgeon and in the presence of a competent anaesthetist.
The patient’s compliance to instructions given by the surgeon is also essential, including:
- stopping smoking 1 month before and after the intervention (reduction of all risks);
- not taking aspirin for 10 days before and after the intervention (reduced risk of hematoma).
The rare complications that could occur include, but are not limited to risk of hematoma, infection, scarring and thrombo-embolic complications (phlebitis) In the event of a complication, appropriate measures will be taken.
• Can the breast lifting procedure prevent pregnancy or breastfeeding?
No. Pregnancy and breast-feeding are possible but can alter the result. A period of 6 months is recommended before or after surgery.
• Can breast sag reoccur after a breast lift?
Yes. With age the breasts tend to sag. Similarly, after pregnancy or weight loss, the results of the operation may be altered.
• Can the procedure be repeated several times?
Yes. A treatment for ptosis can be carried out several times in a lifetime.
• Treatment of Ptosis and breast cancer
The risk of breast cancer is unchanged after a ptosis treatment. In some cases, the treatment of breast ptosis can lead to the discovery of breast cancer, either through systematic analysis of the gland that may be removed (anatomo-pathological exam) or through mammographic assessment conducted generally before the procedure.